One aspect of our health that we often overlook is our gut health, which functions as a linchpin in our overall well-being, influencing everything from digestion to immunity and even mental health. But here’s the thing, we often overlook our gut’s superpowers, and that’s a bit of a problem. So, let’s get friendly with our guts today and explore the superhero world of diagnostic testing. This may sound a bit ‘sciencey’, but stick with me – we’re about to embark on a journey that could be a game-changer for your health. Ready? Let’s dive in!
The Crucial Role of Gut Health

When we talk about gut health, we’re referring to the functioning of the entire digestive system, which spans from the mouth to the colon. Within this system, the gut plays an exceptional role.
The gut, also known as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is a complex system where food is broken down, allowing the absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream. These nutrients – vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins – are the building blocks for your body’s energy, growth, and repair.
But the gut is more than just a food processing facility. It houses an estimated 70-80% of our immune system. This is largely due to the trillions of bacteria residing in our gut, collectively called the gut microbiome. These bacteria interact with immune cells and directly influence immune response.
Moreover, the gut microbiome is also responsible for producing some essential nutrients, including certain B vitamins and vitamin K. B vitamins play a crucial role in brain function and energy production, while vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health.

The Connection between Gut Health and Disease
There is an ever-growing body of scientific evidence that highlights the connection between the state of our gut and the development of several diseases. The gut-brain axis, for instance, is a well-documented concept, showing how gut health can influence mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Poor gut health has been linked to a host of conditions, including:
1. Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) are directly linked to gut health.
2. Metabolic Disorders: Research has shown a connection between gut health and metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
3. Autoimmune Diseases: The gut microbiome’s role in the immune system suggests a link between gut health and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and type 1 diabetes, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Gut dysbiosis is often found in those with thyroid disease, like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease (more on these below). Poor gut health may impair thyroid function, and poor thyroid function can contribute to inflammation and ‘leaky gut’.
4. Neurological Conditions: Emerging research in the field of neurogastroenterology has found links between the gut microbiome and neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, as the autonomic nervous system connects the gut to the brain, so when one is affected, it can impact the other. For instance, one of the first telling symptoms of Parkinson’s can be chronic constipation.
5. Mental Health: The gut-brain axis connection also implicates gut health in mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression. The gut provides approximately 90% of total body serotonin. Lack of enough serotonin is thought to play a role in depression, anxiety, mania, and other health conditions.
6. Skin Conditions: There is also a gut-skin axis, with poor gut health linked to skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Overall, ensuring good gut health is fundamental to maintaining overall health and preventing a range of diseases. Understanding the status of your gut through scientific testing is an important step in the journey to optimal health.
Type 1 – Stool Culture Test
Understanding the Stool Culture Test
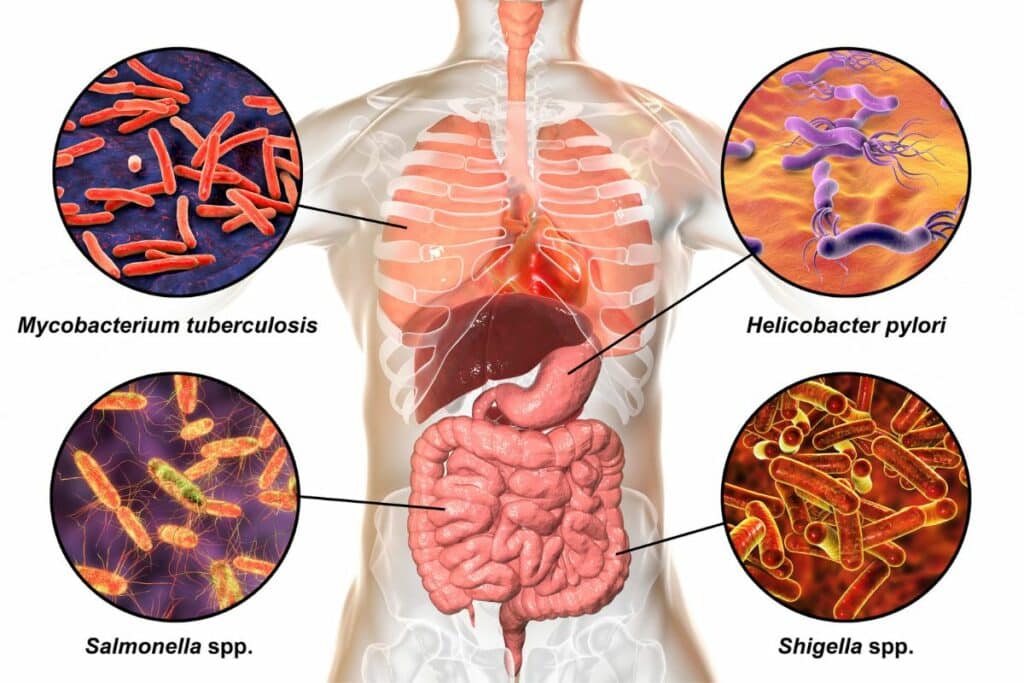
The stool culture test is a powerful tool for assessing gut health. It primarily measures the presence of pathogenic or harmful bacteria, yeasts, viruses, and parasites in your stool sample. It’s like conducting a criminal investigation inside your gut – identifying the potential culprits behind your gut health issues.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of what the stool culture test measures:
1. Pathogenic Organisms: The test detects harmful organisms such as Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, and certain strains of E. coli that can cause severe gut infections.
2. Parasites and Yeasts: The test can also uncover the presence of parasites like Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium parvum, and yeasts like Candida species, which can lead to various digestive issues.
3. Antibiotic Susceptibility: If harmful bacteria are found, the lab can run further tests to determine which antibiotics or antifungals are most likely to be effective against these bacteria.
4. Presence of Blood: Although not its primary function, a stool culture can also detect blood in the stool, which can be a sign of various conditions, including gastrointestinal bleeding or hemorrhoids.
The stool culture test is crucial for gut health because a healthy gut is all about balance. We have both beneficial and potentially harmful bacteria in our gut, but problems arise when this balance is disrupted, leading to a condition known as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is associated with a range of health problems, including digestive issues, obesity, depression, and even autoimmune diseases.
By identifying the presence of harmful organisms, the stool culture test provides invaluable insight into the state of your gut health, helping us create a targeted treatment plan to restore balance in your gut microbiome. It can serve as a critical first step in your journey to optimal gut health.
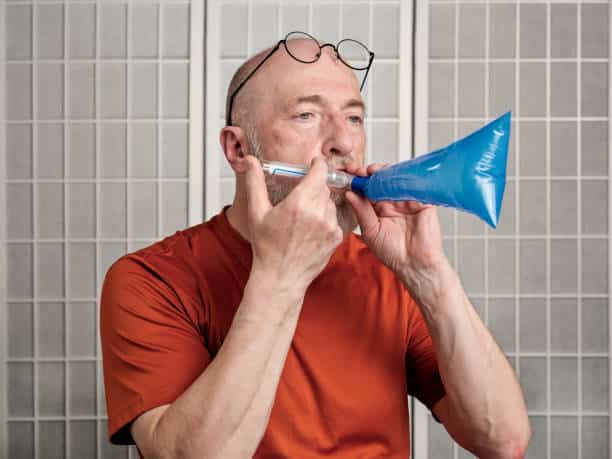

Type 2 – SIBO Breath Test
Understanding the SIBO Breath Test
The Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) breath test is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect an overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine. In a healthy gut, the small intestine contains relatively few bacteria compared to the large intestine. However, when there’s an overgrowth, it can cause various digestive issues. This makes the SIBO breath test a significant part of gut health testing.
The Science Behind SIBO Breath Tests
The SIBO breath test works on the principle of bacterial fermentation. Bacteria in our gut ferment the food we eat and produce gases as a byproduct. When bacteria overgrow in the small intestine, they ferment sugars (like lactose, fructose, or glucose) much more rapidly, producing higher levels of gases.
There are three gases produced: hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and methane. These gases are absorbed into the bloodstream from the small intestine and are then exhaled through our lungs.
By measuring the levels of hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and methane in your breath, the SIBO breath test can indicate whether there’s an overgrowth of bacteria in your small intestine.
Conditions Identified by the SIBO Breath Test
The SIBO breath test primarily identifies Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. However, the symptoms of SIBO can overlap with various other digestive disorders, making it sometimes hard to diagnose.
Symptoms of SIBO include:
1. Abdominal pain or cramping
2. Bloating and excess gas
3. Diarrhea or constipation
4. Unexplained weight loss
5. Malnutrition due to malabsorption of nutrients
Identifying SIBO through the breath test is key as it can be an underlying cause of several conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and certain types of chronic diarrhea.
Process of Undergoing a SIBO Breath Test
The process for undergoing a SIBO breath test is fairly straightforward:
1. Preparation: To ensure accurate results, you will need to follow a specific diet 1-2 days before the test. This diet minimizes the fermentation activity in your gut. It’s also recommended to fast for 12 hours before the test.
2. Baseline Sample: On the day of the test, you will first provide a baseline breath sample.
3. Consuming the Test Sugar: You will then consume a sugar solution, often lactulose or glucose, which will be fermented by the bacteria in your gut.
4. Collecting Breath Samples: You’ll provide breath samples every 15-20 minutes over a 2-3 hour period. These samples will be analyzed for levels of hydrogen and methane.
The test can be conducted at a medical facility or at home with a take-home kit, but not all kits and facilities test for all three gases. Most will only check for Hydrogen and Methane and miss testing the Hydrogen Sulfide. It’s important to know which one you might be dealing with as the treatment differs for each.
Type 3 – Food Allergy Testing
The Link Between Food Allergies and Gut Health
The gut plays a pivotal role in our immune response, including responses to various foods. In some individuals, the immune system mistakenly identifies certain food proteins as harmful, triggering an allergic reaction. These reactions can significantly disrupt gut health, leading to inflammation, altered gut flora, and impaired digestion. Therefore, identifying and managing food allergies is a critical component of maintaining optimal gut health.
What Food Allergy Testing Involves
Food allergy testing typically involves blood tests that measure the amount of specific antibodies, known as Immunoglobulin E (IgE), produced in response to certain foods. When you have a food allergy, your immune system overreacts to a particular food protein and produces these IgE antibodies. The test identifies immediate allergic reactions within minutes to a few hours of eating a food. Symptoms can range from mild (like hives or itching) to severe reactions such as anaphylaxis.
It is often difficult to pinpoint exactly which food causes problems because of the delayed appearance of IgG symptoms. Because of this, an IgG test is the best way to find out what foods you are sensitive to. More practitioners are starting to do IgG testing for this reason.
What FoodConditions Linked to Food AllergiesAllergy Testing Involves
Food allergies can trigger a host of conditions, including:
1. Eczema
2. Asthma
3. Hives
4. Digestive symptoms such as vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea
5. Anaphylaxis – a potentially life-threatening reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
Additionally, some individuals may have food sensitivities rather than allergies, which can lead to conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), migraines, and fatigue.
The Process and Preparation for Food Allergy Testing
The process for food allergy testing is straightforward:
1. Consultation: Shellyr will first discuss your symptoms and medical history. They might ask about the foods you eat, the timing of your reactions, and your family history of allergies.
2. Blood Sample: A blood sample is then taken and sent to the lab to measure specific IgE antibodies and IgM levels. Labs that do both IgE and IgM testing, as well as modification of the foods tested., Many labs only test with raw meat, fish, chicken, and eggs, and not cooked. They may be able to handle it cooked, but not raw. So it’s important to have a complete view of how one can handle some foods better if they are prepared in a certain way, so they can still have it in their diet.
3. Result Interpretation: Shelly will interpret the results, considering your history and symptoms, and guide you on the next steps.
Preparation for a food allergy test is simple. There are no dietary restrictions before the test. However, it’s crucial to keep a detailed food diary leading up to the test, noting any reactions.
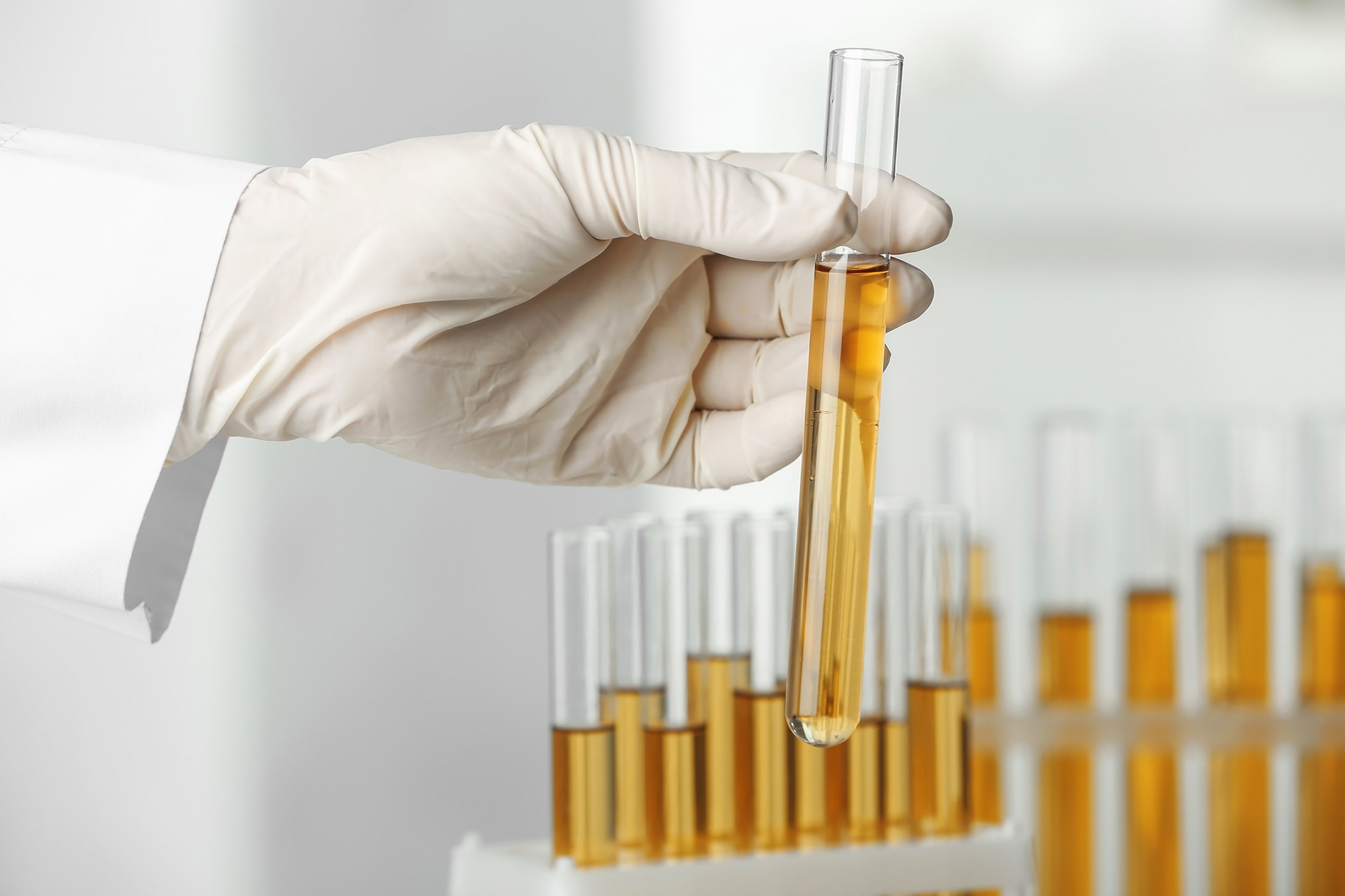

Type 4 – Organic Acid Test
Introduction to Organic Acid Testing
The Organic Acid Test (OAT) provides a comprehensive snapshot of your body’s metabolism. Organic acids are compounds produced during daily metabolic processes, and their levels in urine can provide insight into how your body processes nutrients. This test is significant for gut health, as it can help identify nutrient deficiencies, detoxification issues, and even an overgrowth of yeast or bacteria in the gut.
How Organic Acid Testing Works
The OAT measures the levels of various organic acids in a urine sample. These acids are the end products of metabolism – the process of converting food into energy and other necessary substances.
If certain organic acids are elevated or reduced, it can indicate a metabolic imbalance, a nutrient deficiency, or a problem in the metabolic pathways. For instance, high levels of a specific acid might indicate an overgrowth of a certain bacteria or yeast in the gut.
Insights from an Organic Acid Test
An Organic Acid Test can offer a broad spectrum of information about your overall health, such as:
1. Nutrient Deficiencies: Certain organic acids can indicate vitamin deficiencies and other nutrients.
2. Detoxification Issues: Levels of specific organic acids can show if your body is having trouble detoxifying certain substances.
3. Oxidative Stress: This test can measure oxidative stress markers, a type of cellular damage.
4. Neurotransmitter Metabolism: Some organic acids are byproducts of the breakdown of neurotransmitters and can provide information about brain health.
5. Yeast and Bacterial Overgrowth: Certain organic acids are produced by specific bacteria and yeast species. High levels of these can indicate an overgrowth in the gut.
Preparing for an Organic Acid Test
The process for an organic acid test involves the following steps:
1. Sample Collection: The test involves a simple urine sample, usually collected in the morning.
2. Sending the Sample: The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
3. Result Discussion: You’ll discuss the results with Shelly, who can interpret the data regarding your symptoms and health history.
Before the test, discussing any medications or supplements you’re taking is important, as some can influence the results. Also, you may need to adhere to specific dietary guidelines for 24-48 hours before the test to ensure the most accurate results.
Conclusion
While this blog offers a comprehensive overview of these four predominant gut health tests, it’s crucial to remember that each individual’s gut health needs are unique. Thus, consulting with a functional medicine practitioner, like myself, who can guide you on the most beneficial tests based on your individual symptoms and health history, is paramount.
Understanding your body is the first step in optimizing your health. These tests enable you to uncover essential information about your gut health, equipping you to make informed decisions regarding your diet, lifestyle, and overall well-being.
For any further queries or to book a consultation, please book through the button below. I’m always here to help you on your journey to better health. Here’s to a happy gut and a healthier you!
To shop practitioner-grade supplements at 10% off, use the link below: